Quick Look
Grade Level: 10 (9-11)
Time Required: 45 minutes
Lesson Dependency: None
Subject Areas: Physics, Problem Solving

Summary
Students learn that buoyancy is responsible for making boats, hot air balloons and weather balloons float. They calculate whether or not a boat or balloon will float, and calculate the volume needed to make a balloon or boat of a certain mass float. Conduct the first day of the associated activity before conducting this lesson.Engineering Connection
Engineers apply a solid understanding of the principles of buoyancy in order to design many useful items, such as boats and hot air balloons. Engineers and scientists often use balloons to carry out sensitive atmospheric measurements, including atmospheric wind speed (which can be inaccurate if recorded from a moving airplane), as well as to conduct observations for sensitive areas such as nature preserves. Balloons can fly much higher than airplanes, exiting the first layer of the Earth's atmosphere and flying high enough to see the Earth's curvature. Some balloons reach altitudes of 37 km (120,000 ft). Because balloons are filled with gases naturally found in our atmosphere and do not use fuel to fly, balloons are a "green" way to conduct atmospheric measurements! Plus, most balloons are fitted with GPS tracking systems and tags so they can be returned to the organization that launched them and components can be re-used.
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, students should be able to:
- Determine whether or not an object in air or water will float.
- Given an object's mass, calculate the volume it would need in order to float.
Educational Standards
Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science,
technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards.
All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in TeachEngineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN),
a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org).
In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g., by state; within source by type; e.g., science or mathematics;
within type by subtype, then by grade, etc.
Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science, technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards.
All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in TeachEngineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN), a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org).
In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g., by state; within source by type; e.g., science or mathematics; within type by subtype, then by grade, etc.
Common Core State Standards - Math
-
Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
International Technology and Engineering Educators Association - Technology
-
Students will develop an understanding of the relationships among technologies and the connections between technology and other fields of study.
(Grades
K -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
State Standards
Colorado - Math
-
Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Choose and interpret units consistently in formulas.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
Colorado - Science
-
Newton's laws of motion and gravitation describe the relationships among forces acting on and between objects, their masses, and changes in their motion – but have limitations
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
Worksheets and Attachments
Visit [www.teachengineering.org/lessons/view/cub_balloons_lesson01] to print or download.Pre-Req Knowledge
A basic understanding of algebraic concepts and density.
Introduction/Motivation

(Present this lesson on day 2 of the Balloons activity.)
What makes balloons float? (Listen to student ideas.) Balloons are filled with a gas—such as helium or hydrogen—that is less dense then the air around it, or simply a gas that is hotter than the air around it. If the density of the gas-filled balloon is less than the density of the air it displaces, the balloon will float. So, both balloons and boats float by displacing a more dense fluid with a less dense fluid (both gases and liquids are considered fluids).
Today we are going to see how we can calculate whether or not a boat or balloon will float. An object that floats is said to be buoyant. In this project, your team of engineers has been charged with building an aerial observation device to take measurements of your school. Understanding how to calculate buoyancy will help you in designing your balloon!
Lesson Background and Concepts for Teachers
The buoyant force is the result of an object displacing a fluid (both liquids and gases are considered fluids). If the mass of an object is less than the mass of liquid or gas that the object displaces, the object is said to be buoyant. Buoyancy is a force that is exerted on an object displacing a fluid. Displacing simply indicates that something is being moved out of the way. The amount of buoyancy an object has depends on the density of the fluid it is displacing, and the density of the object. If an object's mass is more than the fluid it displaces, it will sink. Alternatively, if an object has less mass than the fluid it displaces, it will float! To calculate the buoyancy of a solid object, one must know the mass and volume of the object, as well as the density of the fluid it is in. Density is a measure of mass per volume, so dividing an object's mass by the density of the fluid it is in tells you the volume of fluid the object must displace to float.
Example 1: A medical ship has a mass of 100,000 kg. What volume of fresh water (ρ=1000 kg/m3) will the ship displace?
Answer: Since the ship has a mass of 100,000 [kg], it must displace 100,000 [kg] of water to float. To convert this mass to a volume, divide by the density of freshwater (1000 [kg/m3]).
100,000 [kg] / 1,000 [kg/m3] =100 [m33]. Therefore, the ship will displace 100 cubic meters of water.
The amount of water a ship displaces is very important to the ship's captain. If the ship is navigating shallow channels, the captain must know exactly how deep his or her ship is in the water in order to avoid hitting hidden obstacles.
Balloonists must also master buoyancy in order to control how their balloons fly. Most students are familiar with the principle that hot air rises, but how hot must air be to make a balloon fly? Table 1 shows the density of air at various temperatures: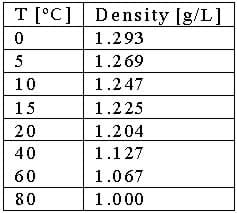
For a balloon of a given mass to fly, the balloon must be full of enough light (less dense), hot air to displace the heavier (more dense), cooler air around it. In order for an object to float, the mass of the object plus the mass of the fluid inside it must be less than the mass of the fluid it is displacing:
M +V ρInside Fluid< V ρOutside Fluid
Where V is the volume of the displaced fluid, ρInside Fluid is the density of the fluid inside the object and ρOutside Fluid is the density of the fluid the object displaces.
Example 2: How large must a hot air balloon be to fly? The inside temperature of the balloon is 80 ºC and the outside air temperature is 15 ºC. The balloon has a mass of 300 kg.
Answer: Rearrange the equation above to solve for V.
First, move the terms containing V to the same side by subtracting V ρInside Fluid from both sides:
M < V ρOutside Fluid – V ρInside Fluid
Next, factor out the V from the right side:
M < V (ρOutside Fluid - ρInside Fluid)
Finally, divide by the difference in the densities:
M / (ρOutside Fluid - ρInside Fluid) < V
Now, insert in the known numbers to solve for V! Refer to Table 1 to find the densities, and remember to convert the mass in kg to grams:
300,000[g] / (1.225[g/L] - 1[g/L]) < V
1,333,333 [L] < V
The answer is 1,333,333 L, (or 1,333 cubic meters). That's a big balloon! What are some things we can do to make the balloon fly better? (Possible answers: Lighten the balloon, raise the inside temperature of the balloon, fly the balloon on a colder day, or increase the balloon's volume.)
Gas balloons work the same way. Different gases have different densities. Some common gasses with densities less than air include helium (ρHelium=0.1786 g/L), hydrogen (ρHydrogen=0.0899 g/L), and neon (ρNeon=0.9002g/L).
Example 3: How much mass can a 10 [L] helium balloon have so that it will fly if the air in the room has a density of 1.2 [g/L]?
Answer: Find the mass of the air displaced by multiplying the density of the air in the room by the volume displaced:
10 [L] x 1.2 [g/L] =12 [g]
Find the mass of the air inside the balloon by multiplying the density of helium by the volume of helium:
10 [L] x 0.1786 [g/L] =1.8 [g]
The maximum mass the balloon can have is the difference between the two:
12 [g]-1.8 [g]=10.2 [g]
Thus, the balloon can have a mass of 10.2 grams and still fly!
Associated Activities
- Balloons - Students follow the steps of the engineering design process to create balloons for aerial surveillance. After a first attempt to create their balloons, they receive the Estimating Buoyancy lesson to learn about volume, buoyancy, and density, which helps them iterate more successful balloon designs. Their balloons carry small flip video cameras to provide aerial images, from which they draw maps and estimate areas.
Lesson Closure
Now that you know how to calculate the buoyancy of an object, you'll be responsible for using these equations to design your own balloons. If you want to use a hot air balloon, calculate how large it must be to lift your device. If you want to use helium balloons, calculate how many helium balloons you need!
Vocabulary/Definitions
buoyancy: Describes whether an object will float or sink in a given fluid.
density: The amount of mass per unit volume (mass/volume).
displace: When one thing moves something else out of the way.
Assessment
Worksheet: After going through example problems as a class, have students complete the three buoyancy problems on the attached Buoyancy Worksheet. Review their answers to assess their mastery of the concepts.
Subscribe
Get the inside scoop on all things TeachEngineering such as new site features, curriculum updates, video releases, and more by signing up for our newsletter!More Curriculum Like This

Students are introduced to Pascal's law, Archimedes' principle and Bernoulli's principle. Fundamental definitions, equations, practice problems and engineering applications are supplied.

Students learn about the fundamental concepts important to fluid power, which includes both pneumatic (gas) and hydraulic (liquid) systems.

The purpose of this lesson is to teach students how a spacecraft gets from the surface of the Earth to Mars. Students first investigate rockets and how they are able to get us into space. Finally, the nature of an orbit is discussed as well as how orbits enable us to get from planet to planet — spec...

Students use modeling clay, a material that is denser than water and thus ordinarily sinks in water, to discover the principle of buoyancy. They begin by designing and building boats out of clay that will float in water, and then refine their designs so that their boats will carry as great a load (m...
Copyright
© 2012 by Regents of the University of ColoradoContributors
Mike Soltys; Marissa H. ForbesSupporting Program
Integrated Teaching and Learning Program, College of Engineering, University of Colorado BoulderAcknowledgements
The contents of this digital library curriculum were developed under a grant from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), U.S. Department of Education and National Science Foundation GK-12 grant no. 0338326. However, these contents do not necessarily represent the policies of the Department of Education or National Science Foundation, and you should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Last modified: November 6, 2019






User Comments & Tips